MODELING THE DYNAMICS OF DIPHTHERIA WITH PUBLIC AWARENESS
Keywords:
Diphtheria, Awareness, Isolation, Reproduction number, Stability AnalysisAbstract
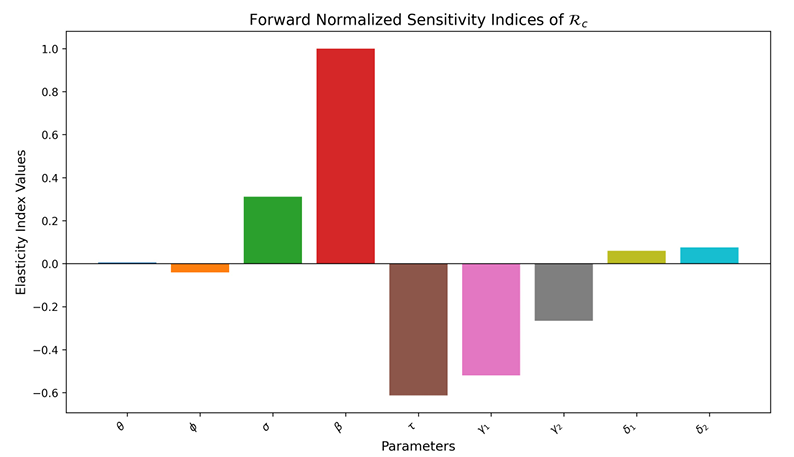
Diphtheria is a highly contagious bacterial infection that primarily affects the mucous membranes of the nose, throat, and airways. It is caused by the bacterium Corynebacterium diphtheriae, which produces a toxin that damages the respiratory system, heart, and nervous system. Despite the existence of effective vaccines, diphtheria continues to pose a threat to global health. In this paper, we developed a nonlinear deterministic model which incorporates public awareness and isolation to describe the dynamics of diphtheria. Analysis of the model reveals that the boundedness and positivity of solutions have been ascertained, diphtheria free equilibrium is both locally and globally asymptotically stable whenever the associated control reproduction number Rc < 1 and unstable when Rc > 1, similarly the endemic equilibrium is globally asymptotically stable when the control reproduction Rc > 1 and ϕ = τ = δ1 = δ2 = 0. Moreover, the model undergoes backward bifurcation in which a stable disease-free equilibrium coexists with a stable endemic equilibrium. The epidemiological implication of backward bifurcation is Rc < 1 is necessary but not sufficient condition for control of diphtheria even when the classical requirement are satisfied. The most sensitive parameters for the control of the spread of diphtheria are identified by forward sensitivity index method and found that contact rate β and progression rate of exposed individuals to infected compartment are the most sensitive parameters for increasing the transmission. On the contrary, isolation rate τ and recovery rate of infected individuals γ1 are the most sensitive for reducing the spread...
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
Copyright (c) 2025 Abbas Abubakar, Aliyu Ahmad, Sani Musa, Ya,u U. Ahmad, Aliyu Abba, Lawan Abdullahi, Jibrin Y. Musa, Wakili Abubakar

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
How to Cite
Most read articles by the same author(s)
- Usman Abubakar, Abdulhamid Ado Osi, Yusuf Ibrahim Muhammad, Ilyasu Abubakar Salisu, Abba Bello Muhammad, Nura Muhammad, Wakili Abubakar, COMPARISON OF THREE DISTRIBUTION FREE CLASSIFICATION TECHNIQUES APPLIED TO CRIME DATA OF NIGERIA PRIOR AND POST COVID-19 PANDEMIC , FUDMA JOURNAL OF SCIENCES: Vol. 8 No. 1 (2024): FUDMA Journal of Sciences - Vol. 8 No. 1
- Usman Abubakar, Abdulhameed Ado Osi, Iliyasu Abubakar Salisu, Hassan Muhammad, Yusuf Ibrahim Muhammad, Abbas Abubakar, ARCSINE RAYLIEGH PARETO DISTRIBUTION: PROPERTIES AND APPLICATION TO CARBON FIBERS DATA SETS , FUDMA JOURNAL OF SCIENCES: Vol. 8 No. 2 (2024): FUDMA Journal of Sciences - Vol. 8 No. 2
- Abbas Abubakar, H. I. Ibrahim, G. T. Adejare, NEWSPAPER COVERAGE OF FOOD SECURITY AND CLIMATE CHANGE ISSUES. A CASE STUDY OF NIGERIAN DAILY NEWSPAPERS , FUDMA JOURNAL OF SCIENCES: Vol. 9 (2025): FUDMA Journal of Sciences - Vol. 9 April (AHB Special Issue)
- Abbas Abubakar, Aliyu Ahmad, Sani Musa, Ya'u U. Ahmad, Usman Abubakar, ASSESSING THE IMPACT OF BOOSTER VACCINE AND ISOLATION ON THE TRANSMISSION DYNAMICS OF PERTUSSIS: USING MATHEMATICAL MODELING APPROACH , FUDMA JOURNAL OF SCIENCES: Vol. 9 No. 8 (2025): FUDMA Journal of Sciences - Vol. 9 No. 8
- Aliyu Ahmad, Abbas Abubakar, Sani Musa, Ya'u U. Ahmad, Aliyu Abba, Lawan Abdullahi, Jibrin Y. Musa, Muttaka A. Shitu, MATHEMATICAL MODELING AND ANALYSIS OF HUMAN TO HUMAN SHIGELLOSIS TRANSMISSION WITH PUBLIC ENLIGHTENMENT , FUDMA JOURNAL OF SCIENCES: Vol. 9 No. 11 (2025): FUDMA Journal of Sciences - Vol. 9 No. 11




