ANALYSIS OF COMORBIDITY IN ENDOCRINE DISRUPTORS OF POLYCARBONATE PLASTICS AND HYPERGLYCAEMIC AGENT IN MALE WISTAR RATS
Keywords:
Polycarbonate plastic, Bisphenol, Streptozotocin (STZ), Endocrine disruptorAbstract
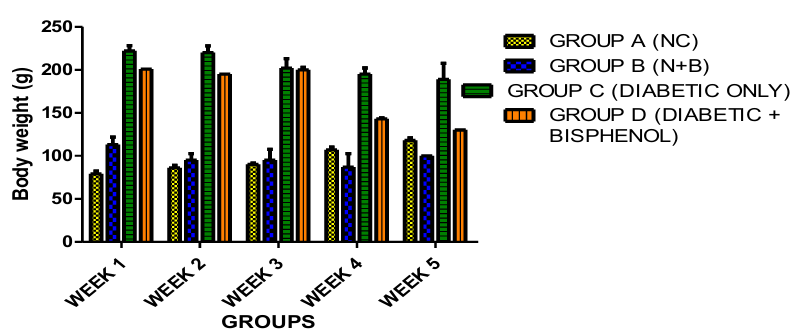
Polycarbonate plastics, widely used in consumer products, contains bisphenol A (BPA), a compound with endocrine-disrupting properties. BPA exposure has been implicated in exacerbating metabolic disorders, including diabetes. Understanding its histological impact on diabetic patients is critical, as chronic exposure may amplify cellular damage. This study employs an animal model to investigate the effects of BPA on diabetic tissues, focusing on histological alterations. Thus, the aim of this research is to elucidate the potential risks of polycarbonate plastic exposure for diabetic individuals. A total number of Twenty male Wistar rats which average weight was 185g were used and randomly splitted into four groups with each group comprising of five rats. Group A served as the control group, Group B were induced with Bisphenol- A (100mg/kg), Group C were induced with STZ (100mg/kg) which served as diabetic group, Group D were induced with Bisphenol-A (100mg/kg) and STZ (100mg/kg) which served as diabetic and bisphenol group. Bisphenol administration was done orally and STZ administration done intraperitoneally. The findings of this study revealed the histological damage caused by bisphenol-A (BPA), highlighting the serious health risks it poses upon entering the body. Specifically, chronic BPA exposure in adult rats was shown to have observable adverse effects, including significant reproductive alterations that could potentially result in infertility. Additionally, BPA exposure led to a marked reduction in body weight and an increase in fasting blood glucose levels. Chronic exposure to bisphenol-A induces histological damage, reproductive alterations, body weight reduction, and elevated fasting blood glucose, posing significant health...
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
Copyright (c) 2025 Adebiyi Aderinola Adegoke, B. J. Dare, D. A. Adekomi, J. O. Fatoki, T. O. Ajadi, A. S. Ebiwonjumi, W. A. Ojo, A. A. Ajayi, A. O. Ajayi, T. A. Oni, O. G. Ojo, T. M. Odutola, L. G. Ogungbe

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
How to Cite
Most read articles by the same author(s)
- O. M. Olayiwola, K. S. Adekeye, F. S. Apantaku, A. O. Ajayi, O. A. Wale-Orojo, I. A. Ogunsola, B. Hammed, INTEGRATION OF BAYESIAN MODEL AND ADAPTIVE CLUSTERED SAMPLING INTO CONTACT TRACING TO CURB THE SPREAD OF COVID -19 CASES , FUDMA JOURNAL OF SCIENCES: Vol. 5 No. 1 (2021): FUDMA Journal of Sciences - Vol. 5 No. 1
- M. S. Olakunle, A. O. Ajayi, M. M. Alfa, A. A. Ahmadu, DEVELOPMENT OF ADSORBENTS FROM RICE HUSK FOR CESIUM REMOVAL FROM SIMULATED WASTE WATER USING CENTRAL COMPOSITE DESIGN , FUDMA JOURNAL OF SCIENCES: Vol. 3 No. 3 (2019): FUDMA Journal of Sciences - Vol. 3 No. 3
- Adebiyi Aderinola Adegoke, Babatunde Joseph Dare, Damilare Adedayo Adekomi, Mayowa Uthman Fadare, Folashade Adekemi Taiwo, Oluwadamilola Oluwatobiloba Amusa, H. T. Adegboyega, M. P. Adio, Adetunji Segun Ebiwonjumi, Waliu Adetunji Ojo, ANTI-INFLAMMATORY ROLE OF ANNONA MURICATA FRUIT EXTRACT ON CYTOARCHITECTURE OF TESTOSTERONE INDUCED PROSTATIC HYPERPLASIA IN MALE WISTAR RAT , FUDMA JOURNAL OF SCIENCES: Vol. 9 No. 6 (2025): FUDMA Journal of Sciences - Vol. 9 No. 6




