INSECTICIDAL ACTIVITY OF METHANOLIC AND ETHYL ACETATE EXTRACTS OF CAPSICUM ANNUUM FRUITS AGAINST AMERICAN COCKROACH PERIPLANETA AMERICANA
Keywords:
Capsicum annuum, ethy-acetate extract, Methanol extract, Cockroach, GC-MS, Fatty acidsAbstract
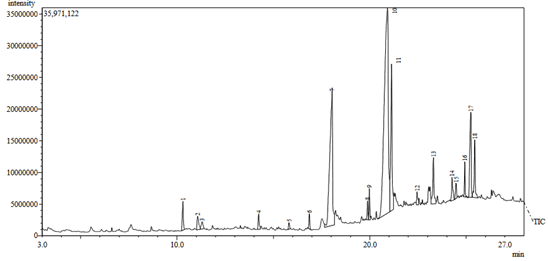
Cayenne pepper (Capsicum annuum) has long been valued for its bioactive compounds, and its potential as a natural insecticide offers a safer alternative to synthetic ones. In this study, the insecticidal properties of cayenne pepper extracts were evaluated against cockroaches (Periplaneta americana L). 35 cockroaches were divided into 7 groups (n = 5), consisting of 1 control and 6 treatment groups. The treatment groups were exposed to the methanolic and ethyl acetate extracts of Capsicum annuum at three concentrations each (20%, 40%, and 80%). Mortality was monitored over 24 hours. Results showed that the methanolic extract caused significantly higher mortality than the ethyl acetate extract, achieving 100% mortality at 80% concentration, whereas the ethylacetate extract induced only immobility and sluggishness at similar doses. GC-MS analysis of the methanolic extract revealed 18 compounds, dominated by oleic acid (44.27%), palmitic acid (20.27%), and capsaicin (6.47%). The insecticidal effects of methanolic extract are attributed to the presence of these fatty acids and capsaicin, while minor compounds, such as terpenoids and fatty acid derivatives, are likely to enhance the efficacy through synergistic effects. This study demonstrates that cayenne pepper extracts, especially those obtained with methanol, could serve as eco-friendly, readily available alternatives to synthetic cockroach control agents. Further studies are needed to explore fractionation of the methanol extract, and more evaluations to validate its potentials in pest management.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
Copyright (c) 2025 Fatimah Opeyemi Roheem, Nura Hamisu

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.




