PHYSICOCHEMICAL PROPERTIES OF YOGHURT PROCESSED FROM THE MILK OF COWS FED CLOVE BUD (Syzygium aromaticum) AND BLACK SEED (Nigella sativa) POWDER AS AFFECTED BY STORAGE
Keywords:
Yoghurt, Clove bud powder, Black seed powder, Physicochemical, AntioxidantAbstract
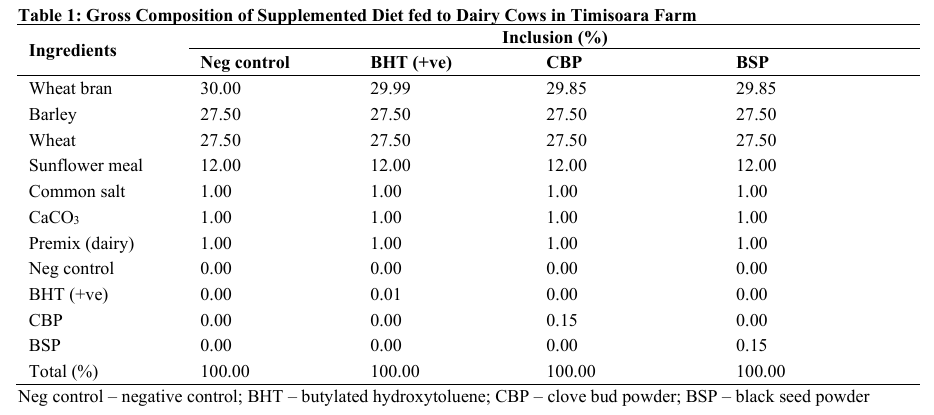
This study evaluated the physicochemical properties of yoghurt processed from the milk of cows fed clove bud powder (CBP) and black seed powder (BSP). Twelve Romanian spotted dairy cows were divided into four groups: negative control, positive control (synthetic antioxidants), CBP and BSP (1.5 % DM) in a completely randomized design. The cows were fed for 21 days, milk collected and processed into yoghurt. The yoghurts were analysed over 28 days of refrigerated storage. Results showed that pH (4.208 to 4.112) and titratable acidity (1.22 to 0.88 %) decreased, while ash (0.640 to 1.300 %), protein (3.068 to 3.435 %), moisture (89.075 to 94.675 %), and fat content (2.478 to 3.850 %) (p < 0.05) significantly increased with storage days (day 0 to 28, respectively). The study concludes that supplementing cow diets with CBP and BSP improved the nutritional profile offering a natural alternative to synthetic additives. For a more nutrient-dense yoghurt, it is recommended that dairy cows be fed up to 1.5 % DM of clove bud and black seed powders.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
Copyright (c) 2025 Aisha Abdulqadeer Muhammad, Shehu Lurwanu Ibrahim

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.




